An energy efficient house should be warm and it should not lose heat. One of the best ways to prevent heat loss is insulating the walls and the roof. The walls lose 15-20% of total heat loss and the roof loses 10-15%. It is important to minimise these losses.
Insulation materials are a significant element of the envelope of a modern building. They assure thermal and acoustic insulation.
Energy efficiency of insulation materials is measured by thermal conductivity coefficient λ which is calculated in Watts per metre per Kelvin degree [W/mK]. In general, a lower λ value indicates a more energy efficient material. The overall heat transfer coefficient (U-value) of the insulation depends on both the thermal conductivity of the material (λ) and its thickness. The U-value characterises the entire insulation. It is measured in Watts per square metre per Kelvin degree W/m2K. Well insulated walls have U = 0,25 and lower, well insulated roofs have a U of less than 0,20.
A wide range of insulation materials is available on the market:
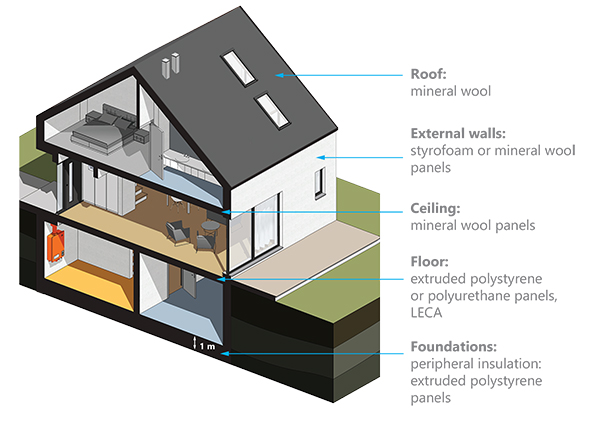
The infographics below present the use of most common insulation materials on individual elements of the house.
Annual costs of heating
Cost of external walls insulation
Cost of ceiling insulation
Annual savings due to ower energy consumption
Brochure „Save energy and the environment”, FEWE
www.termodom.pl
Wspierane przez:
We współpracy z: